- AI Engineering
- Posts
- [Hands-On] Build a Live2D Voice Agent with Real-Time Lip Sync
[Hands-On] Build a Live2D Voice Agent with Real-Time Lip Sync
.. PLUS: Technical rundown of DeepSeek v3.2
In today’s newsletter:
Hands-On: Build a Live2D Voice Assistant with Real-Time Lip Sync
Inside DeepSeek v3.2: A Clear Breakdown of Its Sparse Attention Design
Reading time: 3 minutes.
Imagine building a voice assistant that's more than just audio, one with an animated anime character that moves its lips in perfect sync with speech, reacts naturally, and brings conversations to life.
With the TEN Framework, you can create exactly that: a real-time Live2D voice assistant where animated characters respond to your voice with audio-driven mouth movement and seamless interaction.
In this tutorial, we'll show you how to integrate Live2D models with TEN's voice pipeline to create an immersive conversational experience.
Tech Stack
Project Structure
Backend → The Brain
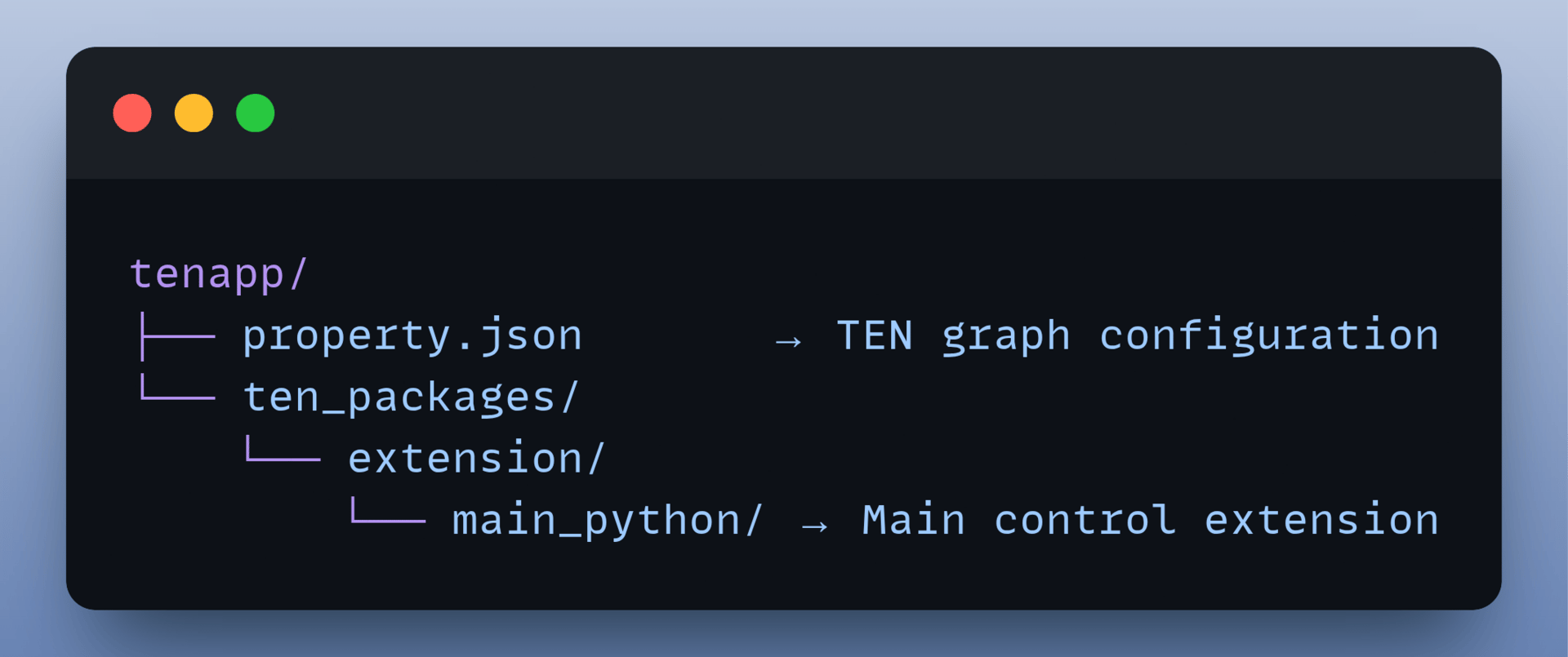
Frontend → The Body
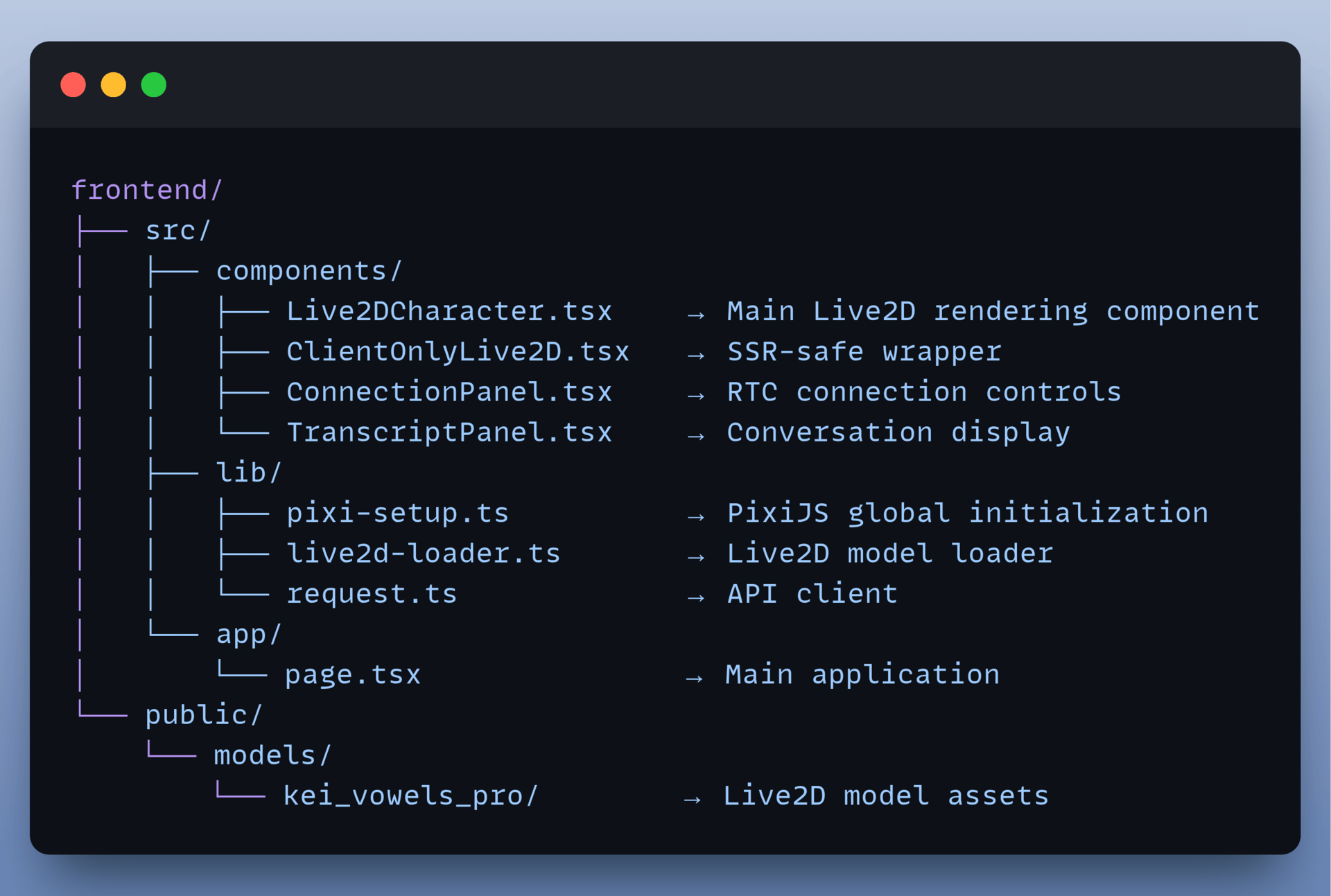
Here's How the Project Works
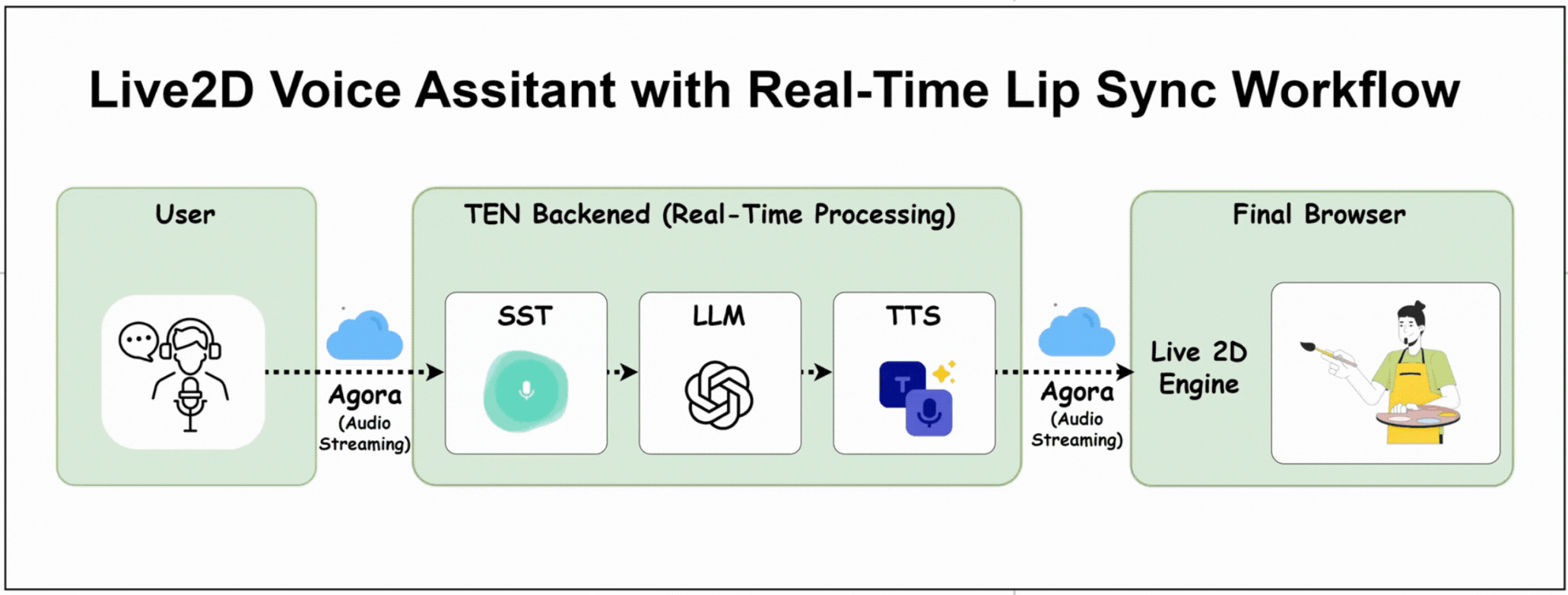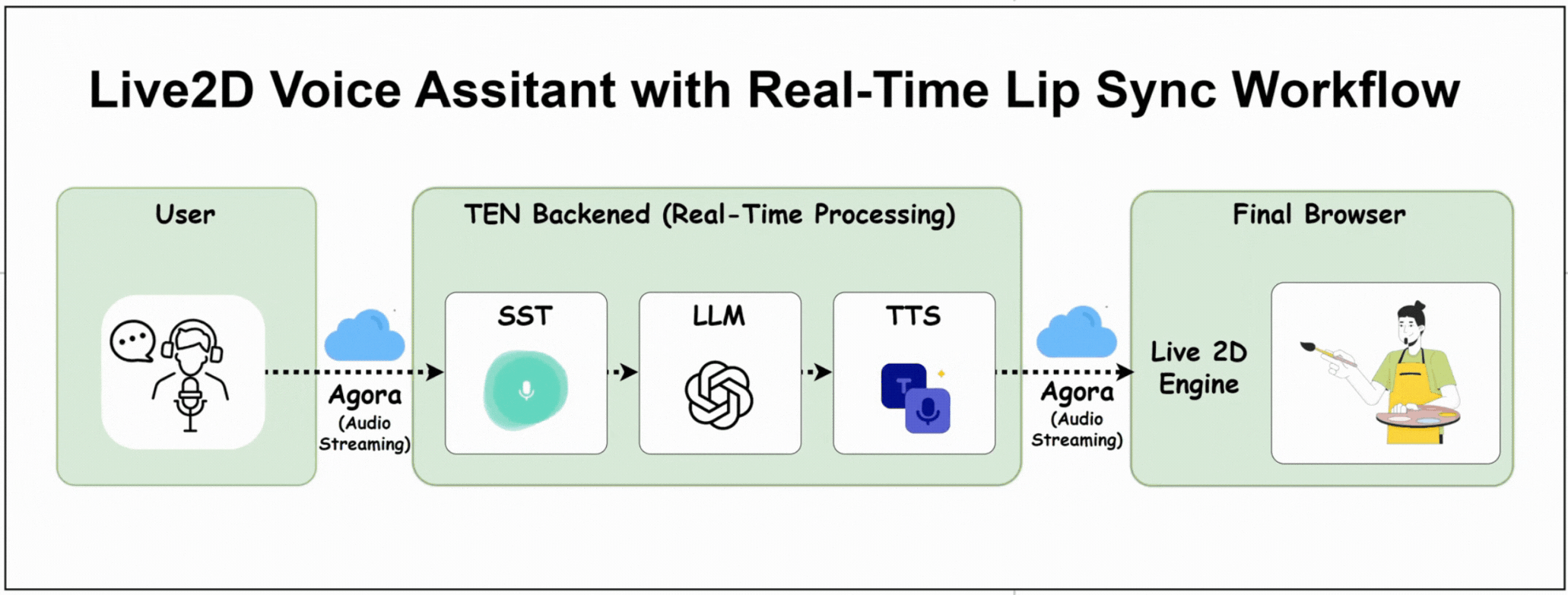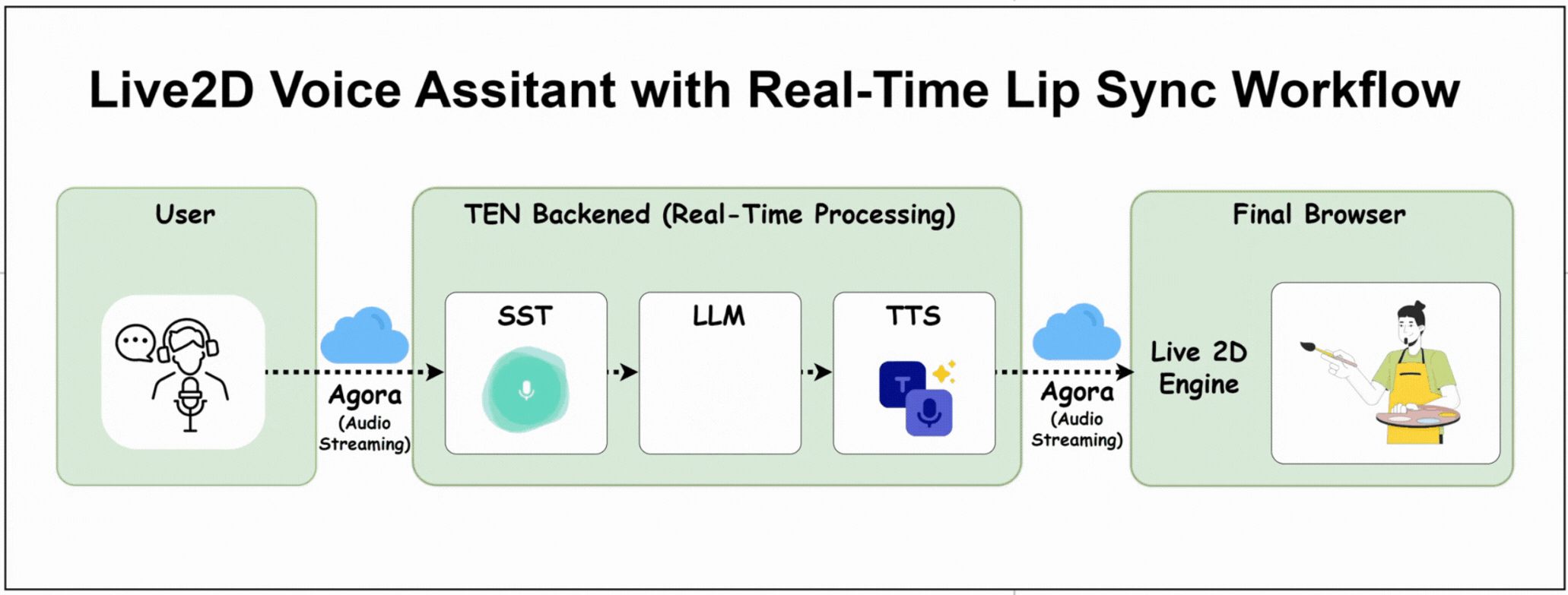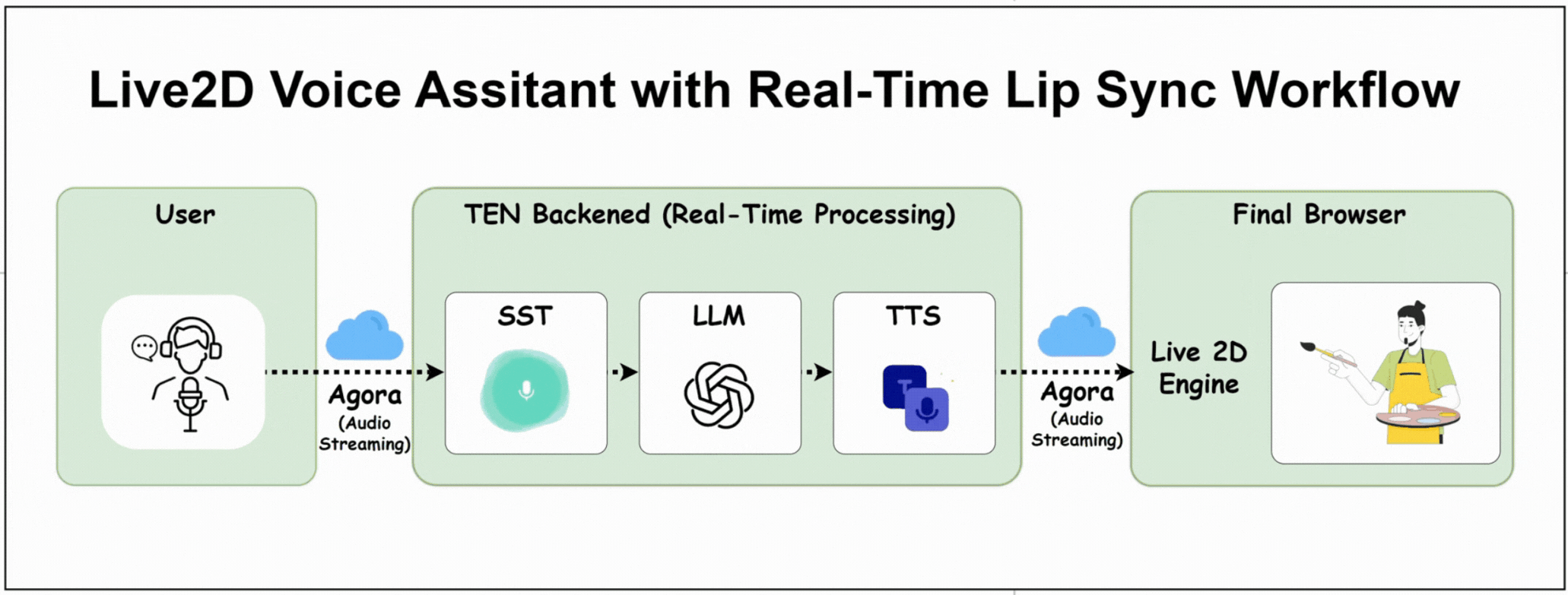
The user speaks into their microphone
TEN backend processes STT → LLM → TTS
OpenAI processes the conversation
TTS generates a voice response
Audio streams back to the browser via Agora.
Live2D character's mouth syncs perfectly with the audio
Character renders with natural animations in real-time
Let's get building:
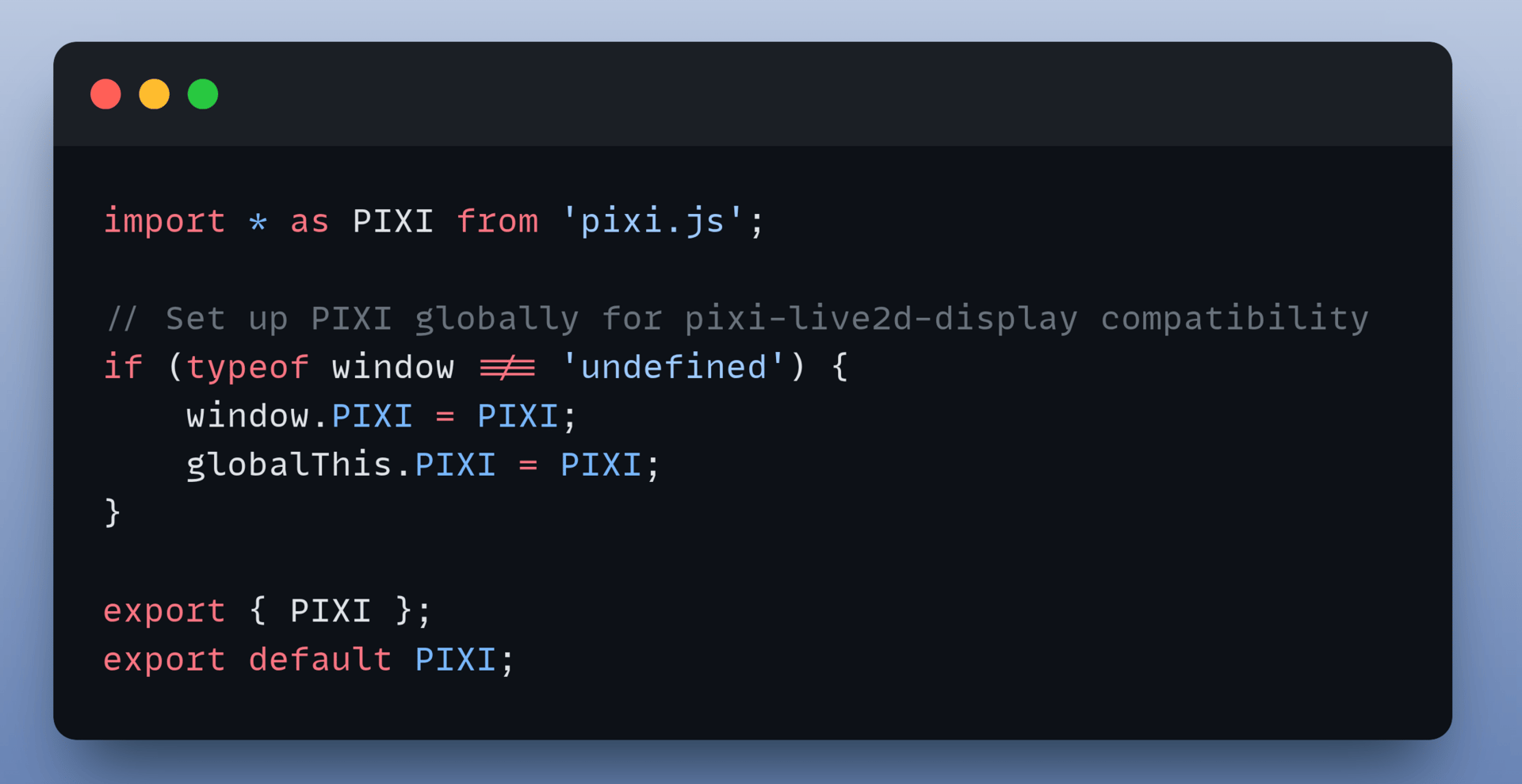
1. Set Up PixiJS Globally
The frontend uses PixiJS to render the Live2D model. However, the Live2D display library expects PixiJS to be available globally before it loads.
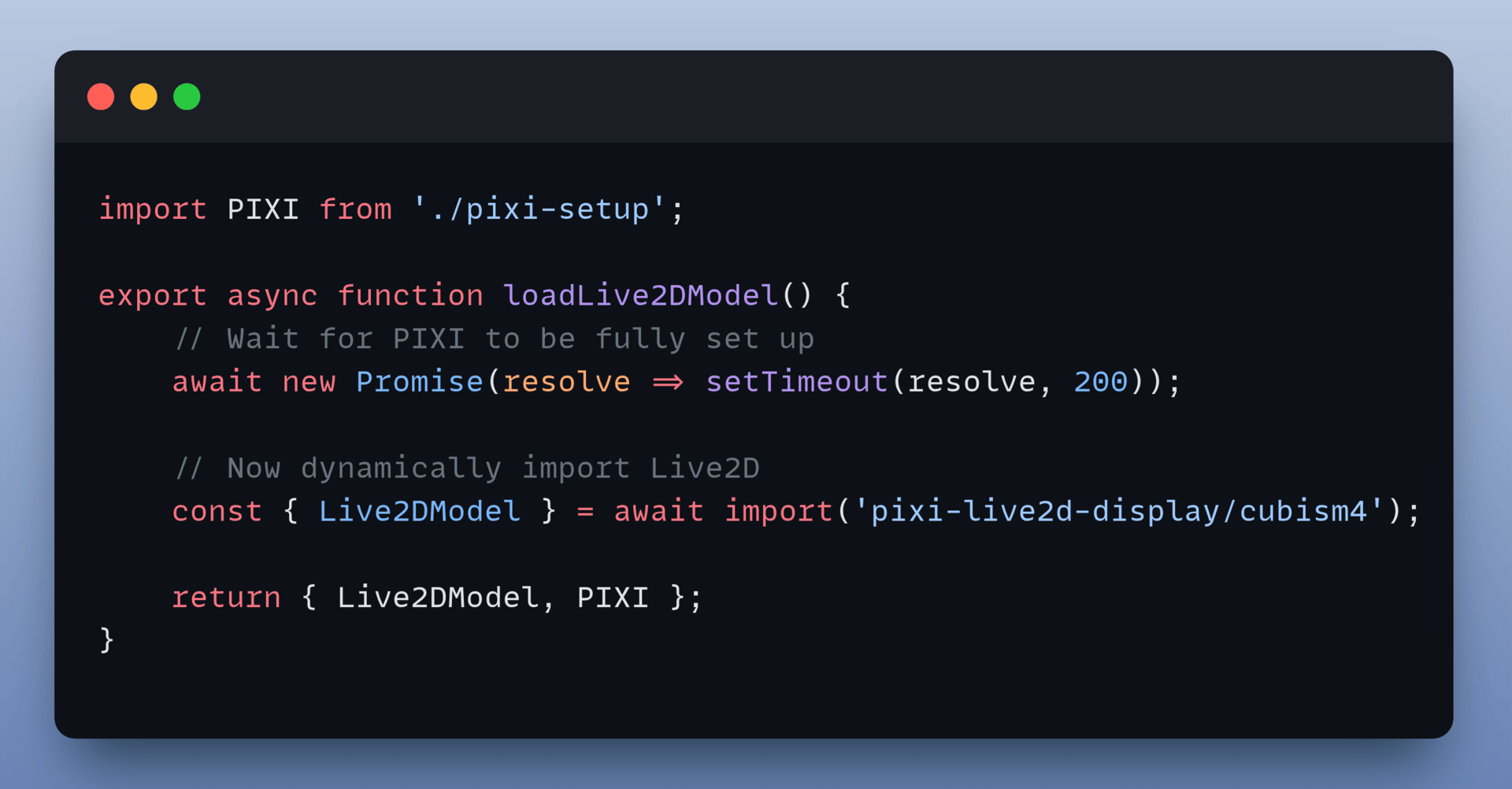
2. Render the Live2D Model
To prevent Server-Side Rendering (SSR) issues and ensure PixiJS initialises first, the system employs a lazy-loading strategy.
The live2d-loader.ts file dynamically initialises the PixiJS application and loads the model.
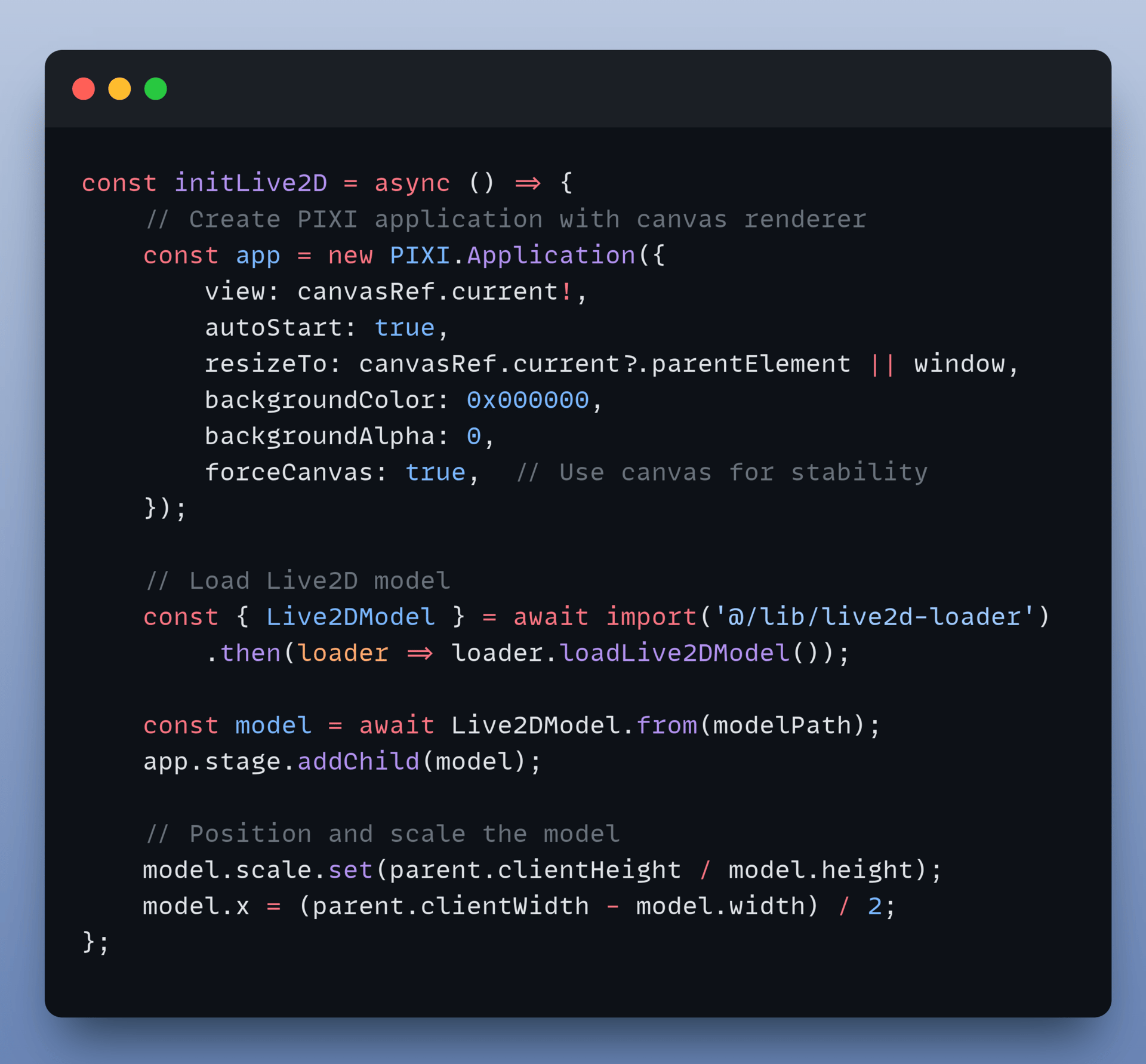
3. Render the Live2DCharacter Component
The main component (Live2DCharacter.tsx) ties the rendering logic together. It initialises the application, loads the model using the loader, and positions the character on the canvas.
Here is the initialisation logic:
4. Implement Real-Time Lip Sync
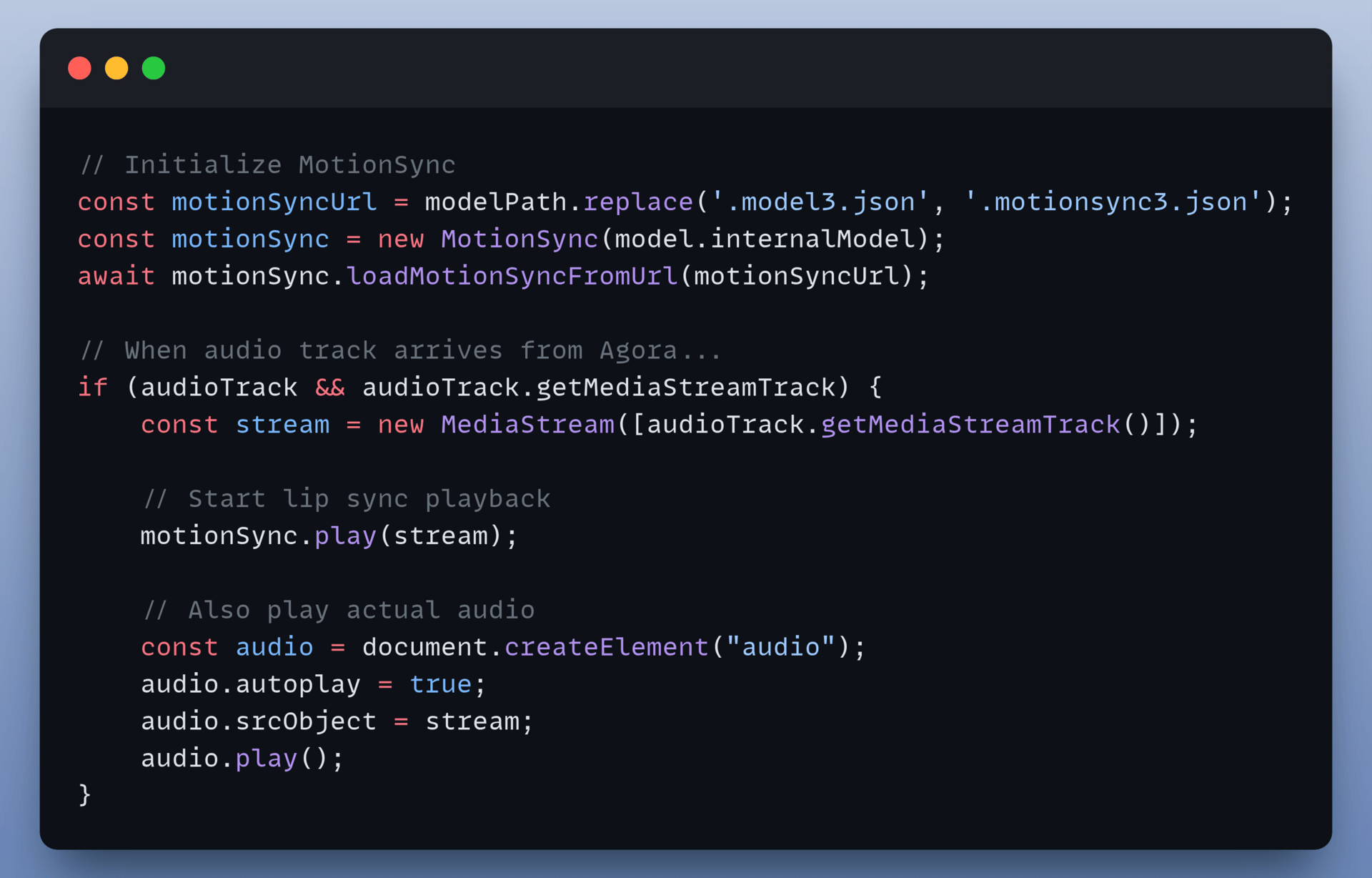
This step gives you the lip movements. Rather than using scripted animations, the mouth moves exactly with the audio returned from the TEN backend.
MotionSync analyses the incoming Agora audio stream and makes the character's mouth move exactly as it "speaks".
Synchronisation logic:
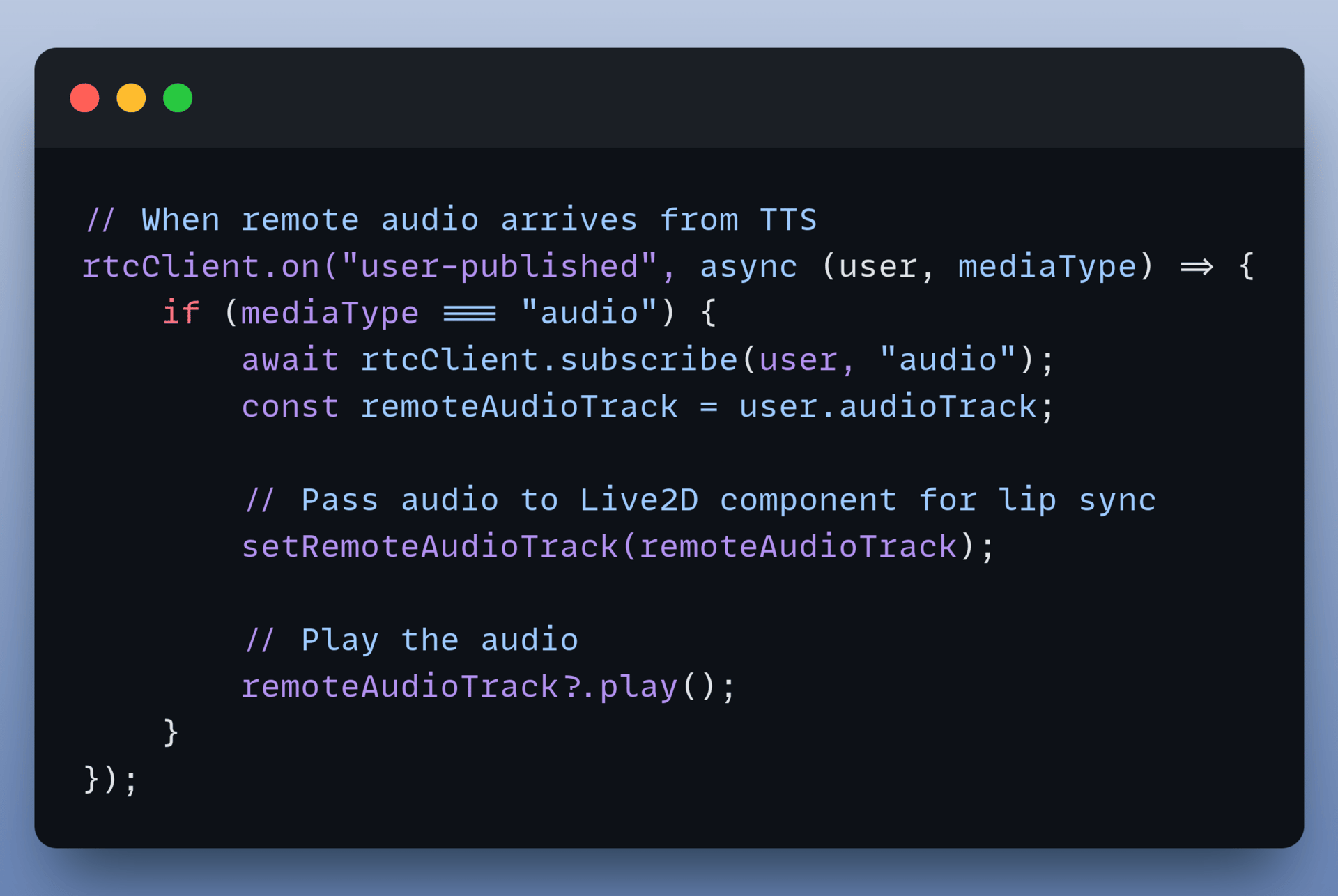
5. Connect Agora RTC Audio
The animation needs audio to work. The system listens for the AI to start speaking through Agora.
This is done using the client-side code in the page.tsx:
Once the audio track appears, pass the captured track into the Live2D component:
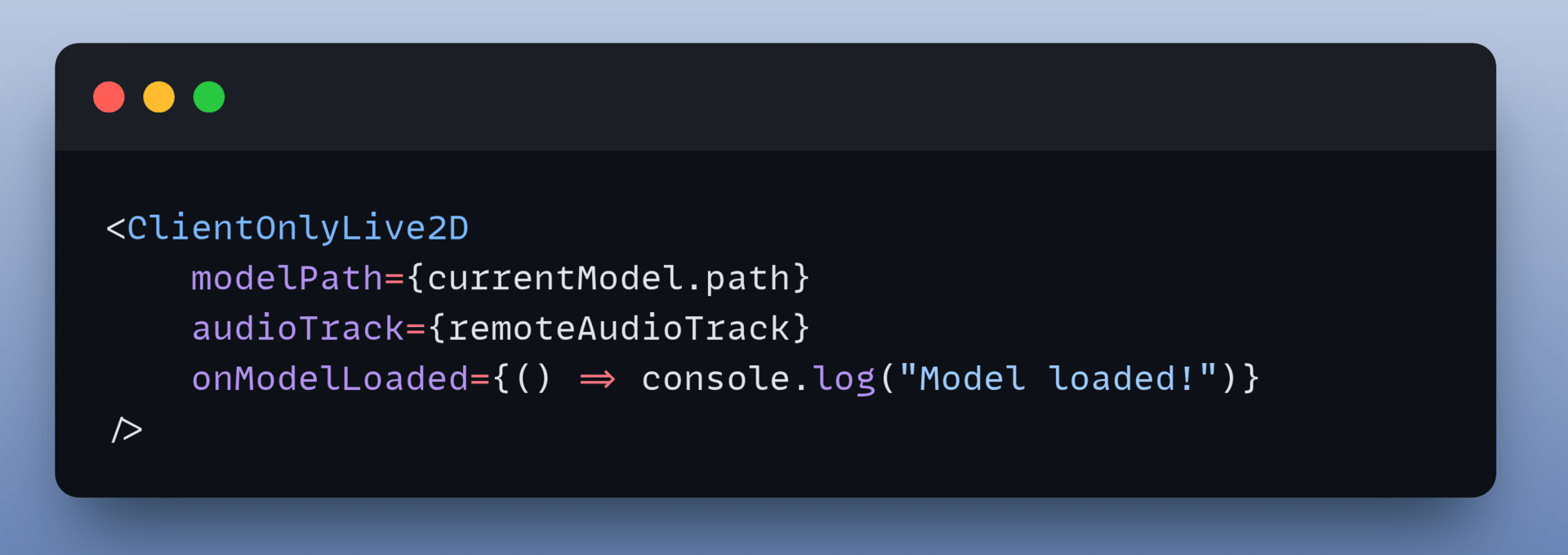
The character automatically syncs its mouth whenever the voice assistant speaks.
6. Handle Server-Side Rendering
Live2D relies on browser-specific APIs that do not exist on the server. To prevent Next.js from crashing during the build process, the system uses dynamic imports to ensure the component only renders on the client.
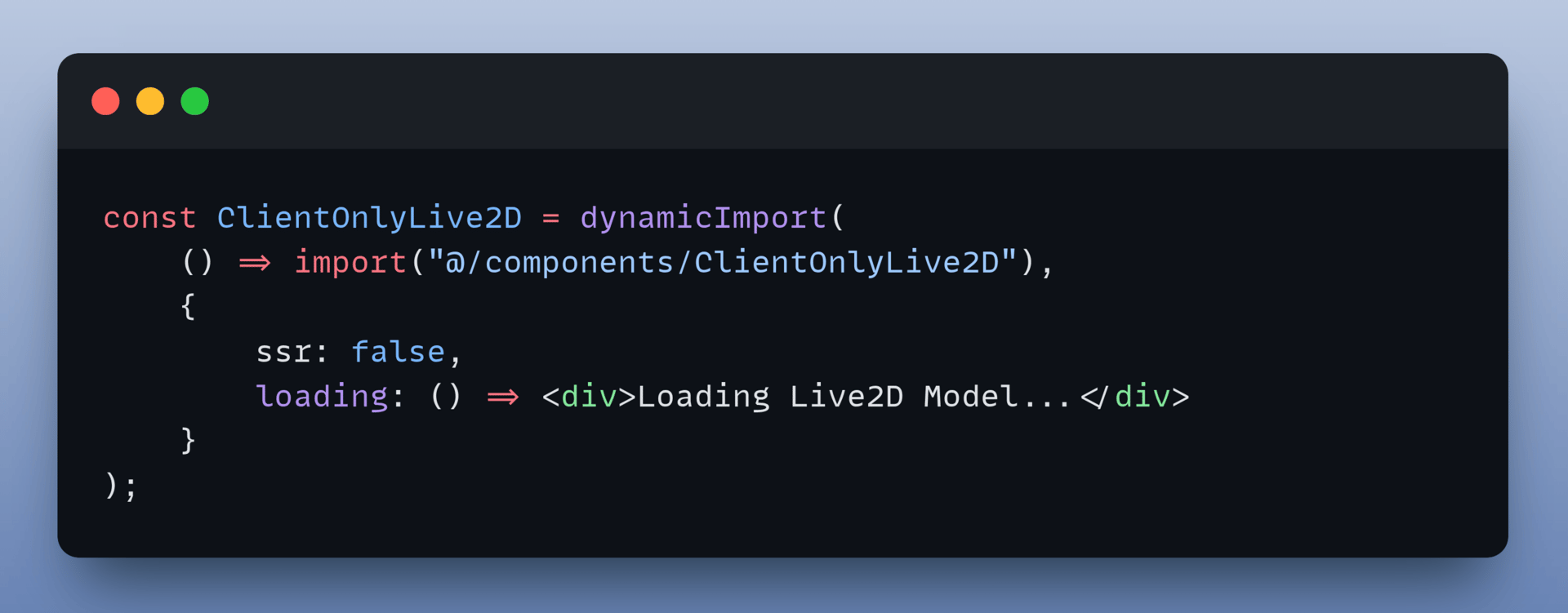
7. Configure and Run
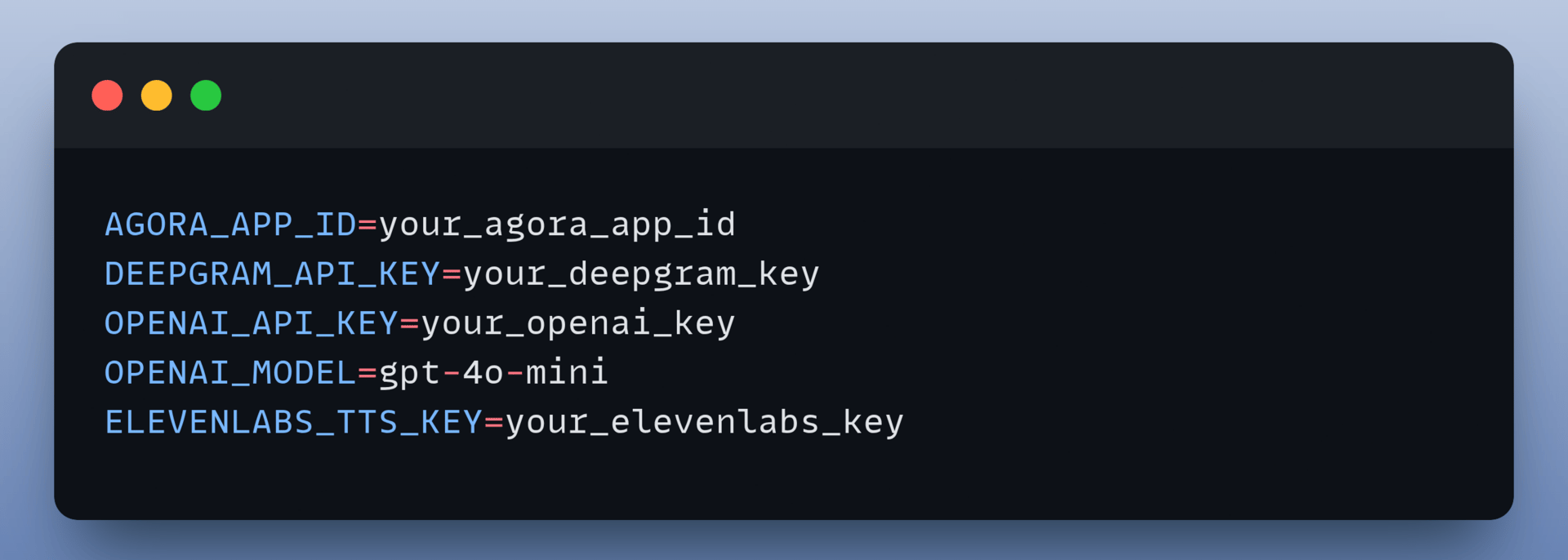
With everything set up, launch your Live2D voice assistant:
Configure your environment variables:
Start the backend:
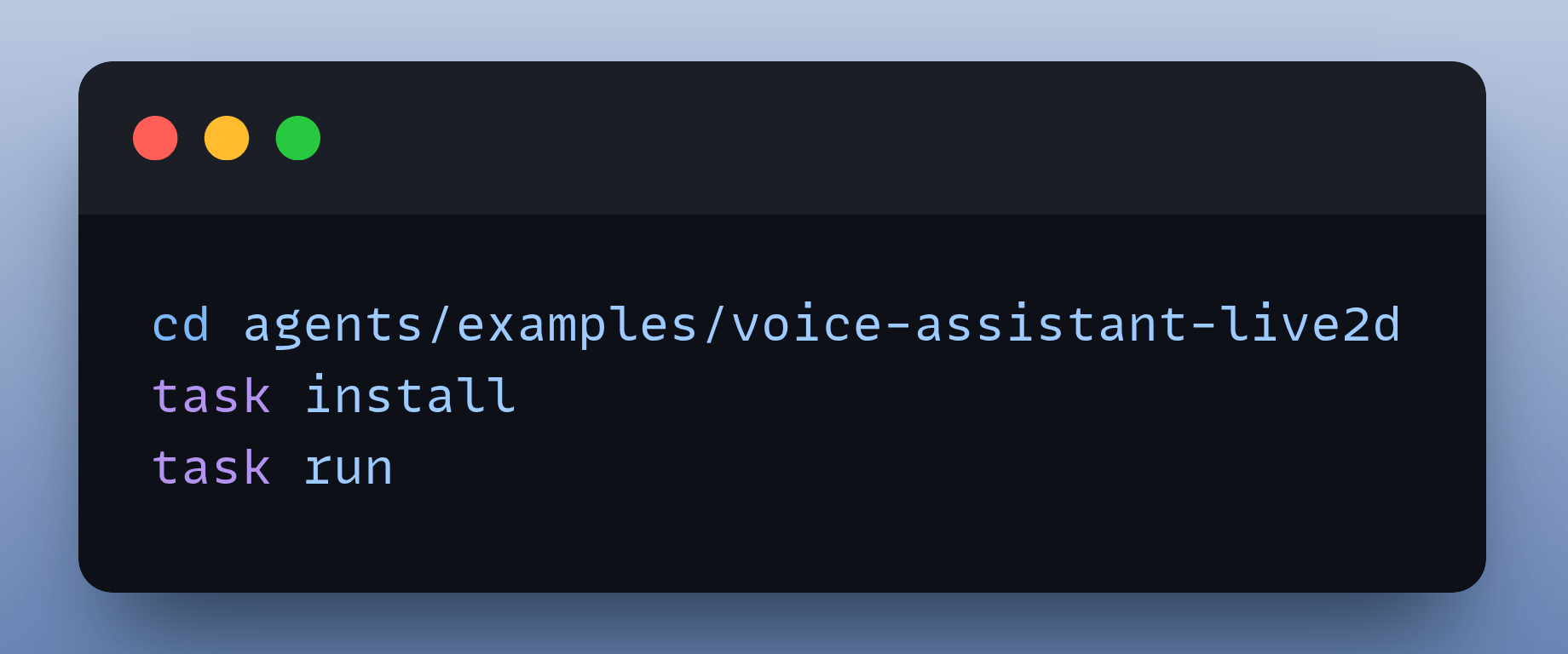
Launch the frontend:
Visit http://localhost:3000, click Connect, and start speaking.
The Result:
The character listens while the user speaks.
The character responds with generated audio.
The lips move in perfect sync with the voice.
Why This Architecture Works?
TEN Framework handles the entire voice pipeline (STT → LLM → TTS) while you focus on creating the frontend.
The backend uses TEN's standard voice pipeline, so you can swap providers (use Azure TTS, Google ASR, Claude, etc.) without changing any code.
AI just had another DeepSeek moment again. With the release of DeepSeek V3.2, this is another breakthrough moment. This has pushed open-source models into performance benchmarks previously dominated by proprietary models.
With their latest release, DeepSeek V3.2 has become the first open-source model to achieve a Gold Medal at the International Mathematical Olympiad, a feat previously attained only by closed-source models.
Elite Reasoning in Two Version Release
DeepSeek releases V3.2 in two official variants, both of which are reasoning-first and are built for agentic use cases, tool use, and long-context workflows:
1. DeepSeek-V3.2: A balanced, general-purpose model optimised for efficiency, fast inference, and strong reasoning performance.
2. DeepSeek-V3.2-Speciale: A high-compute reasoning variant designed for complex logic, advanced math, and agentic workloads.

Benchmark Performance
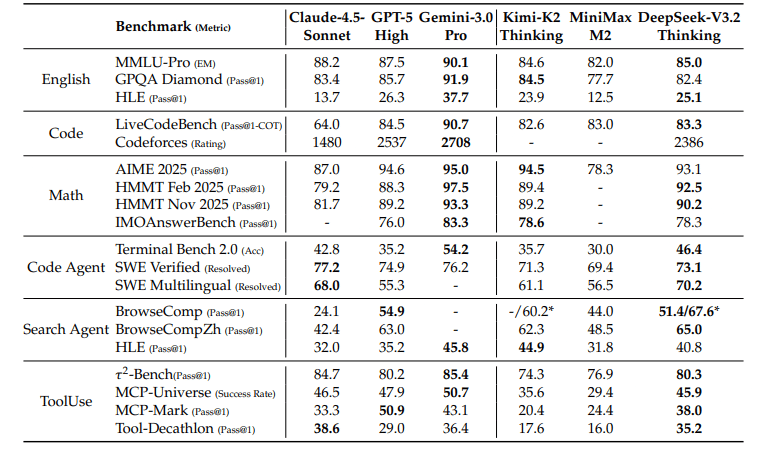
DeepSeek V3.2 beats some major frontier models and delivers exceptional results across major benchmarks.
On AIMI 2025, it takes the lead with the V3.2 Special variant, scoring 96 (Gold Medal), surpassing GPT-5 High at 94.6 and Gemini 3.0 Pro at 95.
On LiveCodeBench, the V3.2 Thinking model posts an impressive 83.3, while V3.2 Special reaches 88.7. And in the GPQA Diamond benchmark, V3.2 Special matches GPT-5 High with a score of 85.7.
Even more impressive, DeepSeek V3.2 model is significantly more token-efficient than GPT-5 High and Gemini 3.0 Pro. The Special version uses more tokens but delivers the model’s highest reasoning performance.
Major Improvements
DeepSeek is known for challenging the status quo in the AI world, and they have made three breakthroughs:
1. DeepSeek Sparse Attention
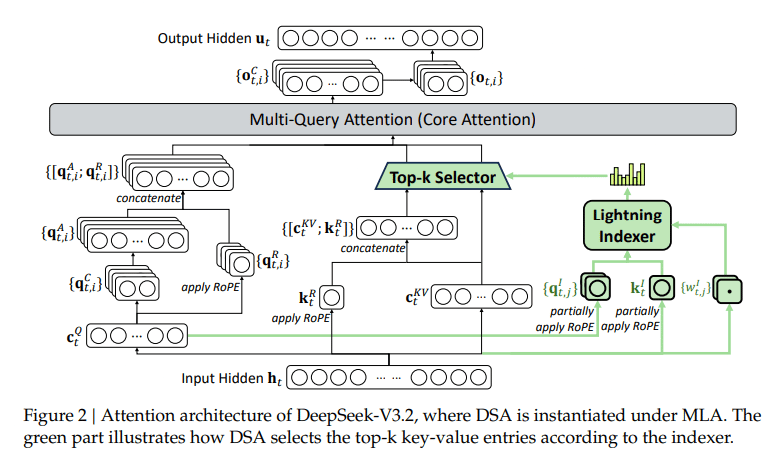
Traditional transformer attention scales at O(L²), which means that as the context window increases, the computational cost also increases quadratically. DeepSeek introduced a new attention mechanism called DeepSeek Sparse Attention (DSA), designed to address this.
DSA reduces this to O(L × K) by letting each token attend only to K important tokens.
In practice, this means:
Long contexts become cheap
Inference gets much faster
Memory usage drops
Models can handle 128K–256K tokens without breaking
2. A Scalable RL Pipeline
Another major leap comes from DeepSeek’s scaled reinforcement learning framework, which upgrades model performance after pretraining. Through a combination of high-quality RL protocols and increased post-training compute, DeepSeek-V3.2 now performs in the same league as GPT-5. This heavy RL powers:
Better reasoning
Stronger tool-use
High competition performance (IMO, IOI, ICPC)
Comparable performance to leading frontier models
3. Agentic and Tool-Use
DeepSeek introduced a large-scale agentic task synthesis pipeline designed to train models to plan, act, and use tools. This allows the model to function more like an actual agent, which is capable of planning, taking actions and using tools rather than just generating text.
This pipeline enables:
Stronger multi-step reasoning
More reliable tool-use execution
Better planning and decision-making
Higher instruction-following
DeepSeek scores high on the tool use benchmark, where it beats most open-source models and performs close to GPT-5 and Claude-4.5 in several categories
Final Verdict
DeepSeek V3.2 is a landmark for the entire open-source AI ecosystem.
The novel attention mechanism and reinforcement learning pipeline represent a major step in taking open source model forward.
If you're building agents or long-context applications, DeepSeek V3.2 is absolutely worth trying.
You can read more about the release here.
That’s a Wrap
That’s all for today. Thank you for reading today’s edition. See you in the next issue with more AI Engineering insights.
PS: We curate this AI Engineering content for free, and your support means everything. If you find value in what you read, consider sharing it with a friend or two.
Your feedback is valuable: If there’s a topic you’re stuck on or curious about, reply to this email. We’re building this for you, and your feedback helps shape what we send.
WORK WITH US
Looking to promote your company, product, or service to 160K+ AI developers? Get in touch today by replying to this email.